Printed circuit board assemblies, sometimes referred to as PCB boards, are at the heart of modern electronics. Found in everything from household gadgets to advanced industrial machinery, these essential components facilitate the functionality of countless devices. But what exactly is a PCB board, and how does it work? Let’s delve into the basics.
What is a PCBA or PCB Board?
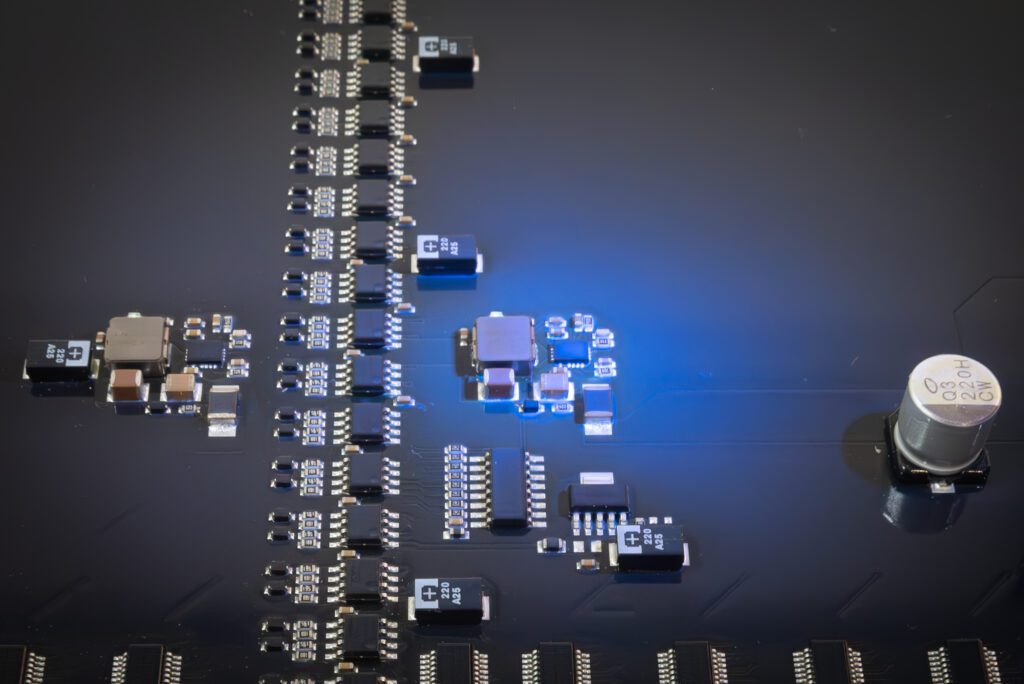
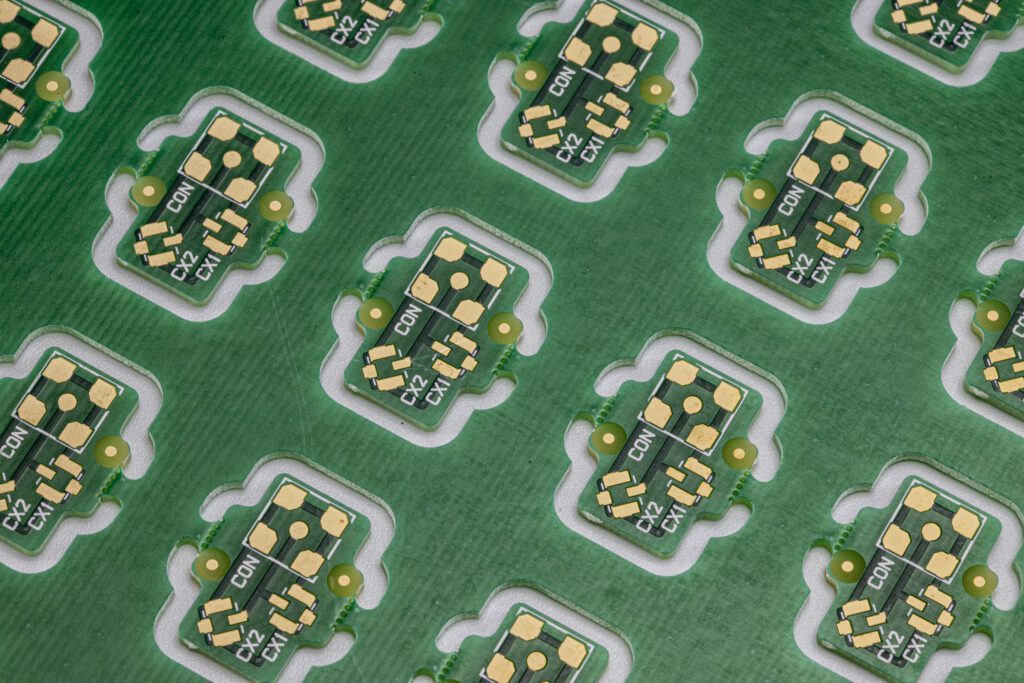
A PCB board, or printed circuit board, is a flat, thin board made from a non-conductive substrate material such as fibreglass or epoxy resin. This is layered with thin sheets of conductive copper, which are etched to create pathways for electrical signals. These pathways, or traces, connect various electronic components, allowing them to work together in a circuit.
Key features of a PCB board include:
- Layers: PCBs can be single-layer, double-layer, or multilayer, depending on the complexity of the circuit.
- Components: Components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits (ICs) are mounted onto the board.
- Solder Mask: A protective layer that prevents unintentional short circuits.
- Silkscreen: Printed symbols and labels that guide assembly and testing.
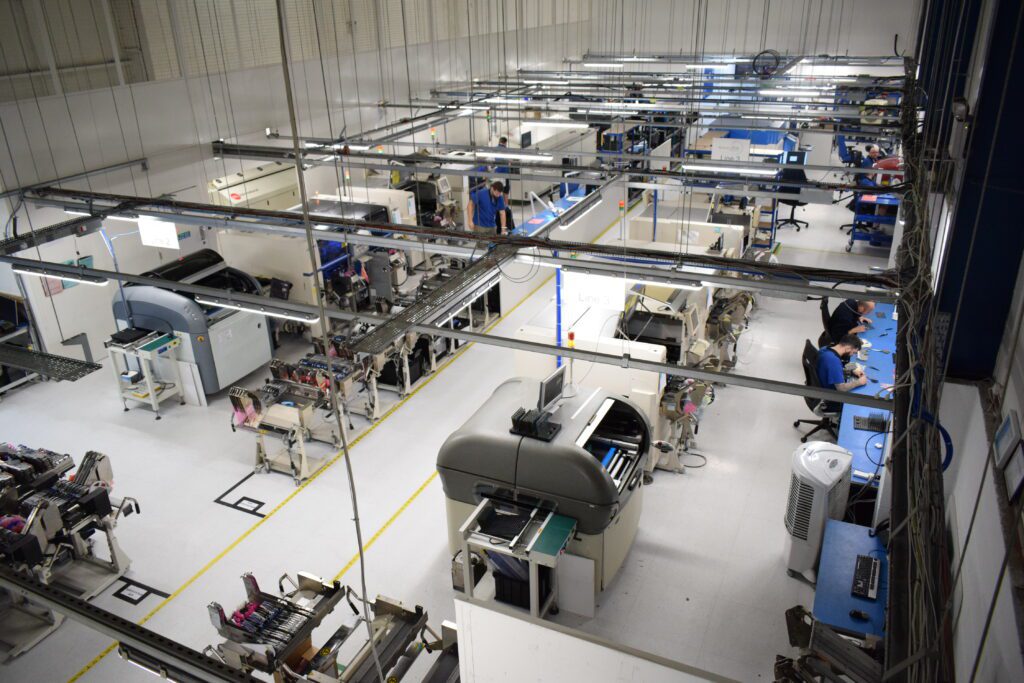
How Does a PCB Board Work?
At its core, a PCB board serves as the physical foundation and electrical interconnection system for electronic components. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Power Distribution: The PCB distributes electrical power from the power source to the various components, ensuring they function properly.
- Signal Transmission: Copper traces on the board act as highways for electrical signals, enabling communication between components.
- Component Integration: Each component has a specific role in the circuit. For instance, resistors control current, capacitors store and release energy, and ICs perform complex computations.
- Mechanical Support: The board provides a stable platform to secure all components in place, ensuring durability and ease of handling.
Types of PCB Boards
PCB boards come in various configurations to suit different applications:
- Single-Layer PCBs: Used in simple devices like calculators.
- Double-Layer PCBs: Found in applications requiring moderate complexity, such as LED lighting.
- Multilayer PCBs: Essential for advanced technologies like computers and communication equipment.
- Flexible PCBs: Allow for bending and folding, ideal for wearable devices.
- Rigid-Flex PCBs: Combine rigidity and flexibility, used in aerospace and medical applications.
Applications of PCB Boards
Printed circuit boards are indispensable in a wide range of industries:
- Consumer Electronics: Things that the average person has in their home – everything from smartphones and tablets to common home appliances.
- Automotive: Engine control units, sensors, and entertainment systems.
- Healthcare: Diagnostic devices, imaging systems, and portable monitors.
- Telecommunications: Routers, modems, and communication towers.
- Industrial Automation: Robotics and control systems.
The Future of PCB Technology
As electronics continue to evolve, PCBs do too. Innovations like miniaturisation, high-speed materials, and environmentally sustainable practices are shaping the future of PCBs.
Flexible and rigid-flex PCBs are becoming increasingly popular in compact and wearable technologies, while multilayer boards enable greater functionality in smaller spaces.
PCB boards are foundational to virtually every device we use. Whether you’re designing a prototype or producing high-volume electronics, PCB boards remain a cornerstone of innovation. For reliable PCB assembly and expertise, contact Active-PCB to see how we can help you bring your projects to life.


